Glance
Exploring quick reading strategies using screen readers
Project Scope: In this project, we investigate how people with visual impairities skim and scan web based data using screen readers. The aim of the study is to present design considerations for screen reading technology that would enable quick reading in web pages that may or may not be semantically organized.
Collaborators: Pooja Upadhyay
My role: Research (conducting scenario based observations), synthesis, generating implications for design
Quick-reading methods (also knowns as skimming and scanning) aim to enhance the rate of reading without compromising comprehension and retention of information. Skimming is a skill that can be helpful in deciding if a text deserves careful reading. Scanning involves searching for specific information. Sighted individuals can visually skim through text content to extract the essence of information. Skimming saves time and reduces cognitive load. However...
...people who are blind do not have the ability to visually skim and scan; instead they use screen readers using multiple strategies.
UNCOVERING USER FRUSTRATIONS
Data Analysis: We organized notes from our study using an affinity mapping method. We organized our notes into recurring patterns in the types of reading strategies our participants used. We combined those patterns into themes based on the intent of the activity.
Methodologies: We observed four participants who are legally blind and asked them to complete task based scenarios.
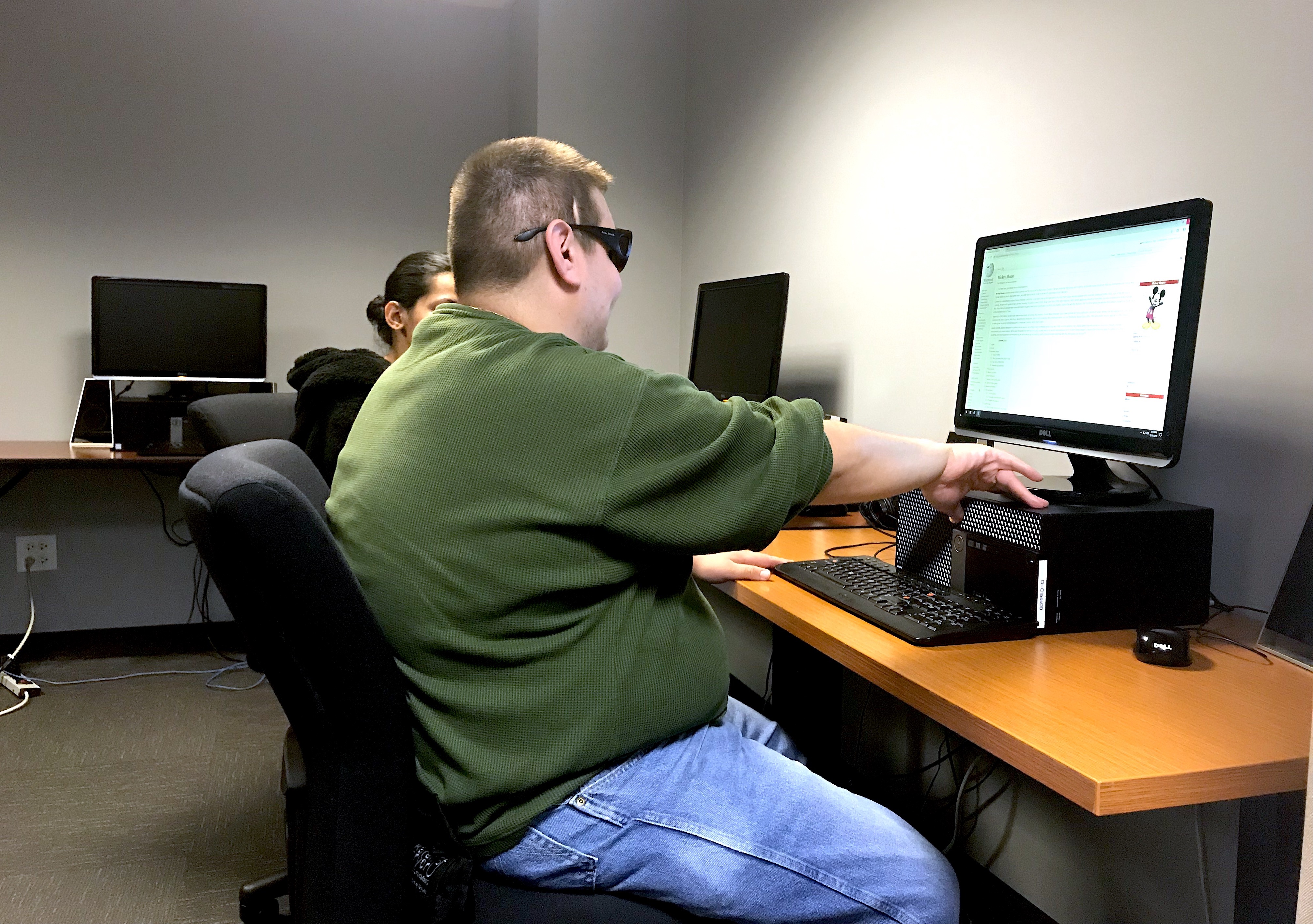

Conducting Observations
All participants are legally blind and are expert screen reader users. Participants had to complete three scenarios using their screen readers of choice.
We presented them with the following scenarios:
1. Go through the webpage and assess whether it is relevant to you; participants were given a xx-minute time frame to complete the task.
2. Go through the section xx to assess whether it is relevant to you; participants were given a xx-minute time frame to complete the task.
3. Find three specific phrases from the xx section; participants were given a xx-minute time frame to complete the task.
After completing the first task, we asked participants what they remembered from the webpage. After each scenario, we asked participants to describe their methods.
After the scenario based task observations, we asked participants how their reading strategies change with different content; specifically ebooks, web pages, emails. At the end of the study, particpants were given a $10 gift card for their participation.
RESEARCH FINDINGS
Findings
We organized notes from our study using an affinity mapping method. Notes were organized into recurring patterns in the types of reading strategies our participants used.
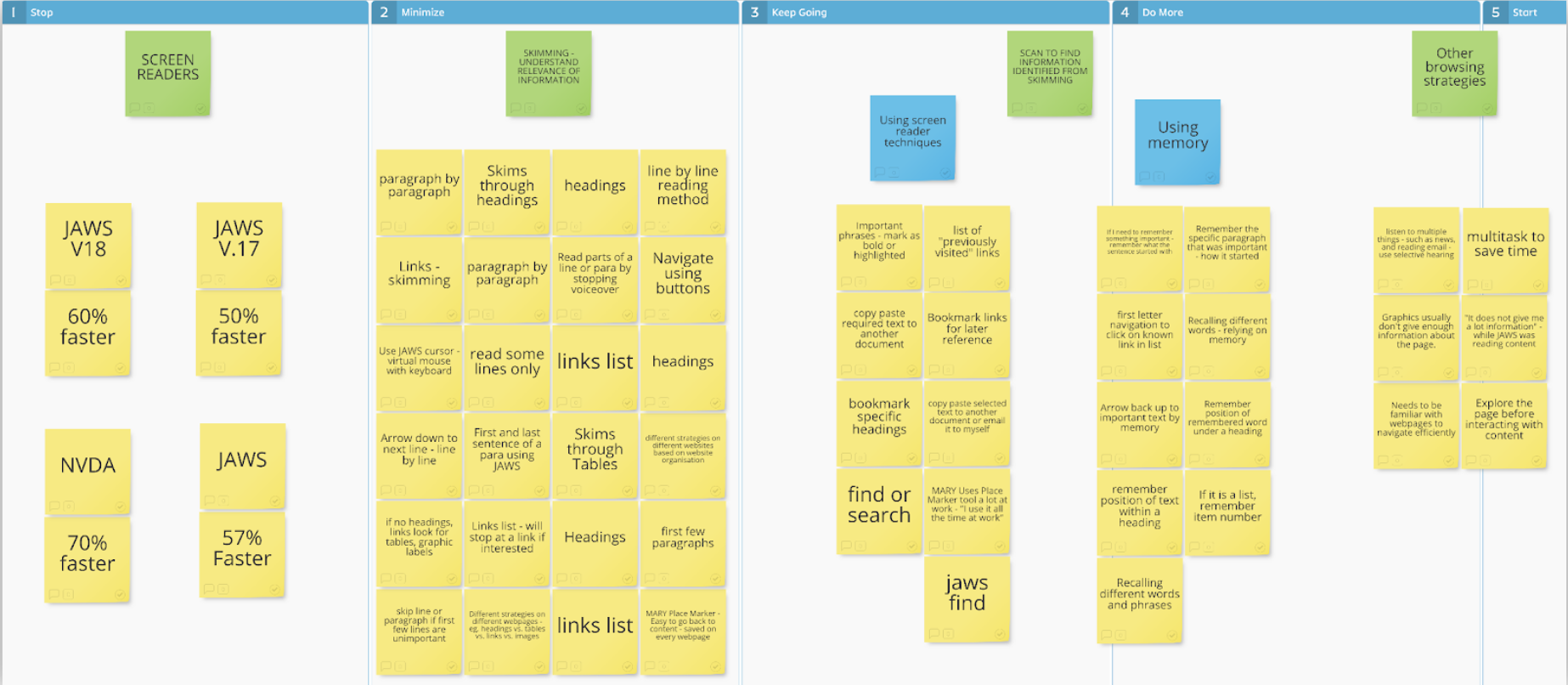
Four central themes emerged:
Skimming through large content/webpage
To navigate through large content, participants used headings, tables, and links.
“Links provide context and help me better understand the page layout.” - Megan
Skimming through small content/section of a webpage
to view shorter content, participants used quick reading strategies such as reading by line or by paragraph
"The fastest way to read a paragraph is to go line by line. I do not have any quick strategies to read specific text." - John
Screen reader affordances
all participants mentioned versions of bookmarking features. Most participants mentioned using the Bookmark feature to save web pages.
"The best way to save a page is to bookmark. Like one normally would." - Lola
Using Memory
all Participants relied on their memory when asked to refer back to a section of the page.
“If I need to remember something important, I remember what the sentence started with.” - Lola
IMPLICATIONS FOR DESIGN

Easy inline bookmarking:
Users should easily be able to assign bookmarks to content on a webpage while reading or skimming. Thereafter, allowing them to retrieve those bookmarks when required, easily. The bookmarks could be numbered for easy identification.
"Skip" Option in Screen Readers
Enable users to skip to the next word, line, paragraph or section, which will allow them to get to the section that they are looking for quickly.
Save to external document
Enables users to select text or content that is relevant to them and automatically copied into a temporary file. Users can access this file to only read the saved sections.
LIMITATIONS + FUTURE WORK
Small sample size (n=4): observing more people in a future study is imperitive to validate current findings.
Narrow age demographic: include participants of a more diverse age group.
Test with different types of web-content; for example, email.

SpringCM, a DocuSign CompanyResearching the prospect customer journey

GlanceExploring quick reading strategies using screen readers

Cal's AngelsScaling the success of partnerships and events

KeepSafeSecurely sharing private content

FlippieEmpowering students in rural India

BurbagA composting solution for community farms

Project ExplorationIncreasing retention of key stakeholders

CareChainFacilitating mental health accountability
DonationsDiscovering charities for donations